
Pesticides are extensively used in agriculture to protect crops, but their environmental release, particularly as mixtures, raises concerns about effects on non-target organisms and ecosystem health. This study aimed to evaluate the toxicity of five pesticides used extensively on soybean crops – glyphosate, 2,4-D, paraquat, chlorpyrifos, and lambda-cyhalothrin- and their binary mixtures on the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, a model organism in toxicology. Our results demonstrate significant reductions in locomotion and body length for all tested pesticides, with synergistic effects observed in binary mixtures. However, the risk-based analysis suggests that the estimated environmental concentrations of these pesticides pose minimal ecological risks. In conclusion, our work highlights the novelty of combining C. elegansbased toxicity assays in a risk-based approach to evaluate pesticide mixtures, offering a practical approach for predicting environmental impacts and promoting sustainable agriculture.
Methods
C. elegans locomotion bioassay. Nematodes were exposed to different pesticide concentrations for 24 hours, and their locomotive activity was recorded to assess acute toxicity. 50 age-synchronized L4-stage nematodes per well were placed in 96-well plates with Leibovitz’s L-15 medium, antibiotics, 5-fluoro-2′- deoxyuridine and cholesterol. Plates were incubated, covered to prevent evaporation and placed in locomotive activity recording equipment (Wmicrotracker ONE, Phylumtech). Locomotive activity data were sampled at 1-min intervals and summed in 30-min bins. Results are expressed as the accumulated activity over 30-min timeframes as a function of toxicant concentration. For locomotive activity-time curves, the area under the curve was calculated for different pesticide concentrations. Each treatment and control had twelve replicates with 50 L4-stage worms per well.
Toxicity treatments. Stock solutions were prepared with M9 buffer (3 g of KH2PO4, 6 g of Na2HPO4, 5 g of NaCl, 1 mL of 1 M MgSO4, and H2O to 1 L, pH 7.2), except for chlorpyrifos, which was diluted in DMSO. Nematodes were exposed to various concentrations of glyphosate, 2,4-D, paraquat, chlorpyrifos and lambda-cyhalothrin made in the M9 buffer. Control groups included nematodes either in M9 buffer without pesticides, or in 0.1 % DMSO for chlorpyrifos treatment.
Results
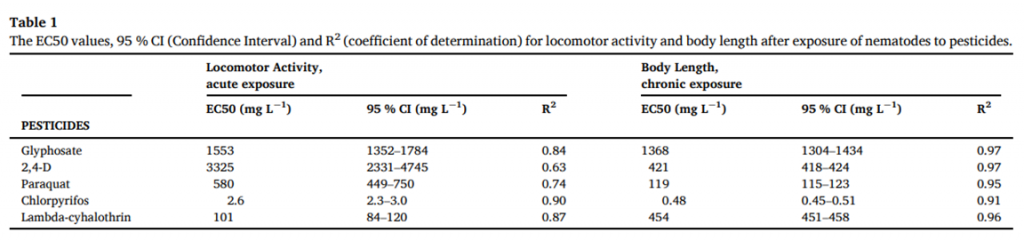
Each of the five pesticides showed significant inhibitory effects on locomotive activity and body length with S-shape concentration-response relationships. Chlorpyrifos had the most significant impacts on both endpoints, causing significant decreases compared with the control at 3 and 0.125 mg L− 1 for locomotion and growth, respectively. This organophosphate insecticide has been previously reported to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE), leading to an accumulation of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. As acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter in C. elegans, its accumulation can lead to severe neuromuscular disruptions and cause the expressive reduction in locomotion and growth that was observed. Glyphosate and 2,4-D herbicides demonstrated the lowest overall toxicity based on both endpoints, whereas paraquat and chlorpyrifos has the most significant impacts on body length. Noteworthy, paraquat has been shown to be less toxic than lambda-cyhalothrin on locomotion activity. Table 1 summarizes the EC50 and associated statistical parameters derived from the adjustment of the log-logistic model of the concentration-response curves. Interestingly, except for lambda-cyhalothrin, growth was a more sensitive response than locomotion.
The use of agrochemical products is crucial to ensure that crop yields meet global food demands. However, these products could pose environmental risks, requiring their safe and sustainable application. This study used two C. elegans toxicity bioassays (locomotion and growth) to assess the acute and chronic effects of pesticides commonly used in Argentine soybean production.
Journal of Hazardous Materials Letters, 2025.
M.I. Manetti, M. L. Migliori, M. F. Kronberg, R. Rota, A. Moya, E. A. Pagano, D. H. Calvo, S. Deglin, M. Embry, D. A. Golombek, E. R. Munarriz.
