
Valproic acid (VPA) is an antiepileptic drug, which is currently used in neurodegenerative diseases. However, a high dose is required to obtain a therapeutic effect. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as omega 3 and omega 6, are efficient complements in treatments for neurological diseases. Based on this, the main goal of this work was to obtain a complex based on VPA encapsulation in an oil/water (o/w) nutraceutical emulsion (NE) enriched with PUFAs for oral administra- tion. Besides, encapsulation of VPA might reduce its dose and increase its therapeutic effect. In order to study its effect, we used a zebrafish larvae model of induced epileptiform behavior with the proconvulsant drug pentylenetetrazol (PTZ).
Materials and Methods:
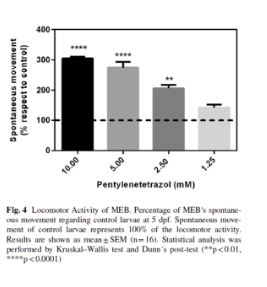
Model of epileptiform behaviour (MEB- Model of epileptiform behaviour) was studied in larvae at 5 dpf, concentrations of different PTZ (1.25, 2.50, 5.00 and 10.00 mM) were tested. Animals were placed in 96-well microplates. This activity was measured for 15 min by the WMicrotracker system, 10 minutes post incubation.
Results:
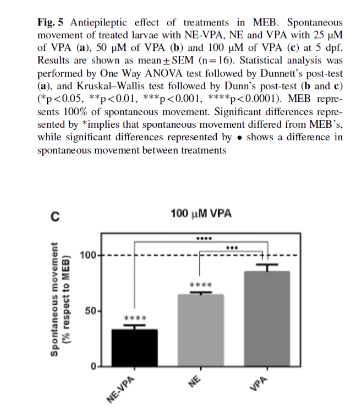
In order to study the antiepileptic effect with VPA was analysed on the MEB defined in the test described above. At 1 dpf, three unhatched embryos were transferred into each well of a 96-well plate containing E3 medium and incubated at 28 °C. At 5 dpf, the following treatments were tested: (i) 25, 50 and 100 μM of VPA in NE-VPA, (ii) NE without VPA, (iii) 25, 50 and 100 μM VPA (iv) control (untreated larvae). Larvae were incubated with treatments during 1 h at 28 °C. After incubation, 2.50 μl of PTZ (2.50 mM) was added in order to induce epileptiform behavior. 10 min later, spontaneous locomotor activity was measured as previously described. 16 wells were used for each treatment.
The study of the Model of epileptiform behaviour (MEB) was dependent on PTZ concentration. The lowest drug concentration that induced epileptiform behavior was 2.50 mM. (fig 4) Thus, this concentration was used in in the evaluation trials of antiepileptic effect with VPA as MEB model.
Treatments with only VPA (fig5) showed small differences in spontaneous movement respect to MEB. On the other hand, treatments with NE-VPA reduced significantly the epileptiform behavior when were compared to MEB. This effect was further observed with 100 μM NE-VPA. Also, treatments with NE decreased larvae spontaneous movement. The reduction exerted by NE-VPA was much more significant than treatments with only VPA.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Nanomedicine & Biotherapeutic Discovery. OMICS Publishing Group. 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2155-983X.1000121.
Maria Jimena Prieto, Nahuel Eduardo del Rio Zabala, Cristian Hernán Marotta, Dario Bichara, Sergio Simonetta, Nadia Silvia Chiaramoni and Silvia del Valle Alonso.
