
Royalactin is a glycoprotein essential for the development of long-lived queen honeybees. Only larvae fed with royal jelly, containing royalactin, develop into queens. Royalactin plays a central role in this process by switching on the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor signaling pathway which ultimately leads to epigenetic changes and a long-lived queen phenotype.
Recently it was shown that royalactin by itself also extends lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster. lifespan. In this assay ,the effects of royalactin on lifespan extension in a non-insect species, Caenorhabditis elegans are reported . Royalactin enhances locomotion in adult nematodes, implying that royalactin also influences healthspan.
Locomotion measurement was made with adult nematodes in wells of a flat-bottom 96-well plate containing 200 μL of S complete medium with a final concentration of 85 μM 5-fluoro-2′-deoxyuridine to prevent self-reproduction, and 5 μL mL−1 nystatin (Sigma, N1638) and 50 mg mL−1 ampicillin to avoid contamination. As a food source we added flash frozen E. coli K12 bacteria until an OD600 of 1.7 was reached. For the treated condition, worms were grown on royalactin-containing NGM plates starting from the L1 stage until transferring them to liquid medium with a final concentration of 1.7 μg mL−1 royalactin. Fourteen wells were used for each condition, with ca. 30 worms in each well. After a recovery period of 3 h, we measured locomotion during 24 h with the WormMicrotracker.
Los resultados obtenidos en presencia de royalactina mostraron un aumento de locomoción en nematodos adultos. Este fenómeno podría reflejar la influencia de la royalactina sobre la vida saludable del nematodo.
In the graph it is compared swimming activity between royalactin-treated and non-treated wild-type worms in early to mid-adulthood. As a positive control we used the hpa-1(tm3256).
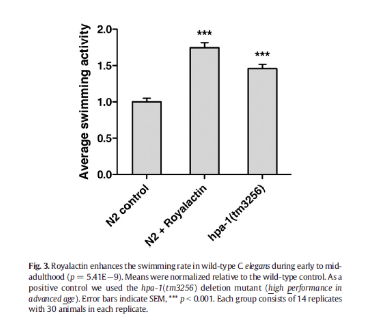
Both royalactin-treated and positive control worms show an increase in swimming activity compared to the wild-type control .Average swimming activity increases with ca. 75% upon royalactin treatment . Additionally, royalactin-treated worms display a significant increase in average swimming activity compared to the positive control hpa-1
The results obtained in the presence of Royalactin showed an increase of locomotion in adult nematodes. This phenomenon could reflect the influence of royalactin on the healthy life of the nematode.
